There are a lot of questions out there about what amino acids are and how they relate to our overall health and well-being. The purpose of this article is to help you develop a basic understanding of not only what amino acids and collagen are, but what they do and why we need them to lead a healthy life.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and structural enzymes in the body. There are 2 main types of amino acids, essential and non-essential. There are 20 amino acids in total, 9 of which are essential amino acids which the body cannot make on its own. Essential amino acids include methionine, lysine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, leucine, isoleucine, histidine, and valine. Three of the essential amino acids, methionine, lysine, and phenylalanine are called branched-chain amino acids and they account for 20% of the amino acids of muscle. A branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) is just that, they have a branched-chain structure.
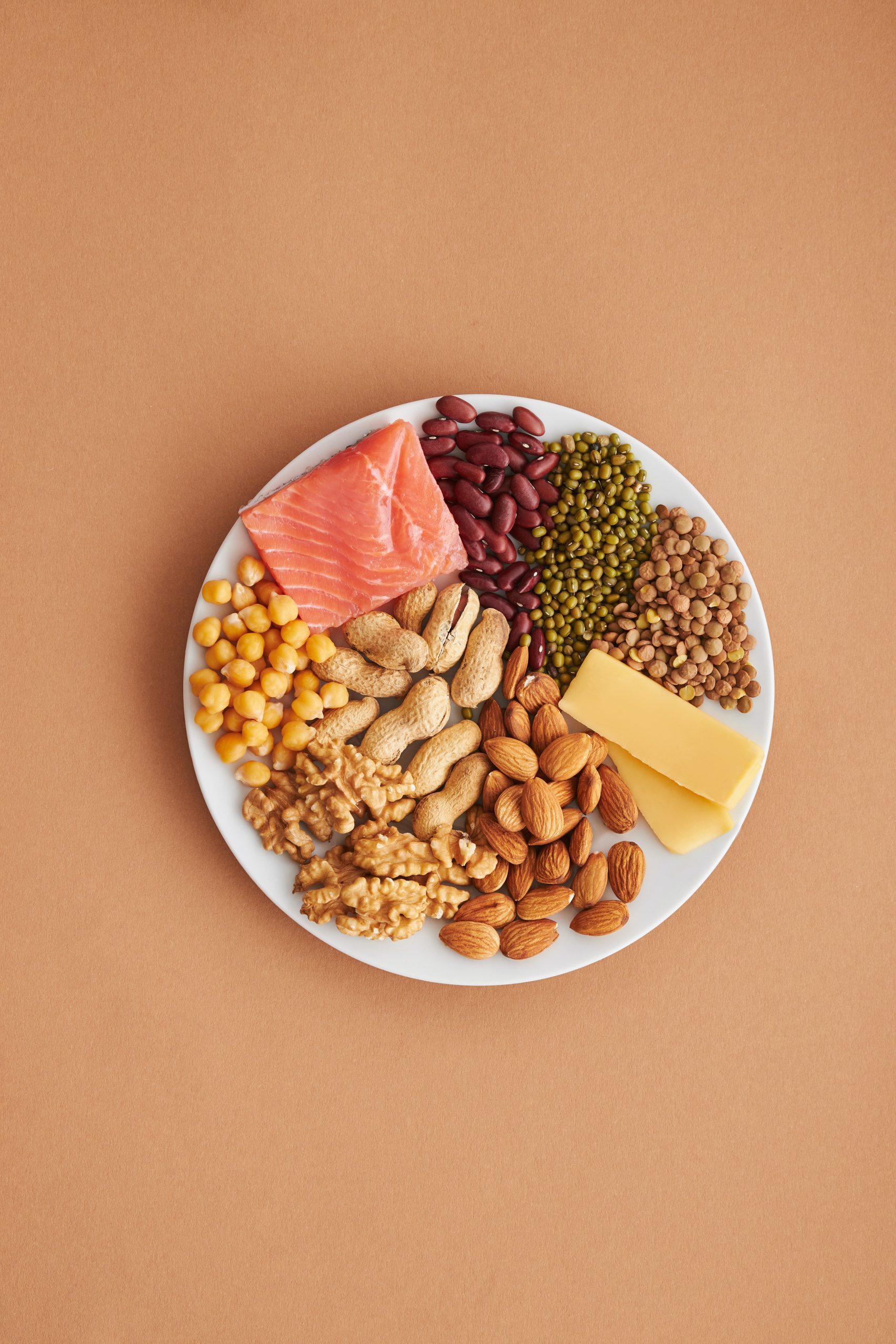
Essential amino acids are required by external sources to form specific proteins in the body necessary for cell development. All 9 essential amino acids are found in red meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and animal milk products which not only come with the amino acids but with B12 which can also be derived from plant sources such as algae, seaweed, and nutritional yeast. Additionally, there are plant sources such as buckwheat, quinoa, spirulina, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and soy that contain all 9 amino acids. Many other plant-based foods have some of the essential amino acids, so combining plant-based foods in the diet such as beans, rice, legumes, lentils, seeds, nuts, chickpeas, broccoli, and spinach will ensure all 9 essential amino acids are being supplied.
The 11 remaining non-essential amino acids include alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. All of the non-essential amino acids are synthesized in the body primarily from glucose with exception of tyrosine which is synthesized by phenylalanine and are therefore not essential in the human diet. The body requires the combination of essential and non-essential amino acids for the building of specific proteins.
The daily recommended value of protein is 46-63 grams per day. A 6-ounce beef steak has almost 49 grams of protein, 2 eggs have just over 12 grams and a single cup of lentils has almost 18 grams of protein. While many plant-based proteins are not as rich in amino acids as animal products and most plant-based foods do not have all 9 essential amino acids, they do come with other benefits such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber to name a few.
Why supplement with essential amino acids?
For many aging people simply consuming protein-rich foods is not enough. The body must break the proteins down into amino acids for absorption. As we age we lose our ability to break proteins down into amino acids. Many vegans do not get the amino acids they need from plant-based foods. A poor diet may also leave one deficient in essential amino acids. Essential amino acid deficiencies due to a restrictive essential amino acid diet or inability to break proteins down into amino acids can lead to a wide variety of health issues including but not limited to muscle wasting, loss of appetite, autoimmune conditions, allergies, fatigue, toxicity, and brain-related conditions.
Collagen Peptides
The combination of essential and non-essential amino acids makes up oligopeptides, peptides, and polypeptides otherwise known as proteins. A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds (2-50 amino acids). Peptides can be subdivided into oligopeptides (2-20 amino acids). A polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids (50-2000 amino acids). Polypeptides can also be called proteins. The largest protein chain in humans is Titin and has more than 27,000 amino acids.

The collagen peptide is the most abundant protein in the animal kingdom including the human body consisting of about a third of the body’s protein composition. Collagen is what holds us together and comes from the Greek word “Kolla” means glue. While collagen is not as complicated as a Titin protein, there are approximately 1,400 amino acids that make up a collagen protein in 3 polypeptide chains wound together in a triple right-hand helix consisting primarily of 3 main non-essential amino acids being glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.
There are 4 group types of collagen in the human body
- Densely packed fibers found in skin, bones, tendons, fibrous cartilage, connective tissue and teeth and represents 90% of your body’s collagen
- Loosely packed fibers found in cartilage which cushions bones
- Structures of muscles, organs, and arteries
- Filtration function within the skin
Why supplement with collagen?
As we age we produce lower quality collagen leading to visible signs of less supple skin and weakened cartilage. People who smoke or have smoked may experience reduced collagen production. Ultraviolet radiation from sunlight reduces collagen production. Too much sugar and carbs interfere with collagen’s ability to repair itself.